Strength Training | Cardiovascular Exercise | High Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) | Rest Days | Example of an Ideal Weekly Training Schedule | FAQ |
Quick Answer
A balanced exercise regime combines 3 strength sessions, 4 Zone 2 cardio sessions, 1 HIIT session, and 1–2 rest days weekly. This approach builds muscle, boosts heart health, enhances endurance, and supports recovery for sustainable fitness and wellbeing.
Introduction
An ideal exercise regime for the average person balances various types of physical activity to promote overall health and fitness. It includes cardio, strength, and flexibility exercises while allowing for adequate rest. This approach helps improve wellbeing without overwhelming your schedule or body. This page outlines a practical exercise plan tailored for the average person’s needs.
Note: The following information outlines the ‘ideal’ training regime, however, any exercise is better than no exercise. Do what works for you, and use the following as a framework to help inform your exercise protocols.
Building an Effective Exercise Routine
Strength Training – 3 Weight Lifting Sessions Per Week
Doing at least three (3) weekly weight lifting sessions targeting all muscle groups optimises your muscle growth, strength and metabolism.
Utilising the concept of progressive overload (the gradual increase in weights lifted) will ensure continued muscle growth over time.
- Increases Strength by progressively challenging your muscles, improving your ability to perform daily tasks like lifting or carrying objects.
- Increases Muscle Mass by promoting hypertrophy and stimulating growth through resistance training.
- Enhances Aesthetic Appearance by toning muscles and reducing body fat, creating a more defined physique.
- Improves Self Esteem and fosters a sense of accomplishment through achieving fitness goals, which improves confidence and mental wellbeing.
- Reduces Chronic Pain by strengthening muscles that support joints, alleviating conditions like lower back pain or arthritis.
- Improves Mobility by enhancing muscle strength and joint stability, making movements like walking or climbing stairs easier.
- Increases Metabolism by improving insulin sensitivity and boosting your resting metabolic rate through muscle growth. This helps regulate blood sugar and supports fat loss.
Cardiovascular Exercise – 4 Zone 2 Cardio Sessions Per Week
Engaging in four (4) Zone 2 cardio sessions per week, such as brisk walking, light jogging, cycling or swimming at a moderate intensity where you can still hold a conversation, improves your heart health, endurance, and overall well-being.
Each cardio session should be 30 – 60 minutes long, with intensity raised or lowered as needed to stay within the zone 2 range.
- Improves Cardiovascular Health by strengthening your heart, improving blood flow, and lowering blood pressure, reducing the risk of heart disease and stroke.
- Increases Fitness & Endurance by improving aerobic capacity, allowing you to perform physical activities for longer without fatigue, such as climbing stairs or walking long distances.
- Enhances Lung Health by improving oxygen uptake and circulation, reducing shortness of breath during exertion and supporting overall respiratory function.
- Boosts Mood by triggering endorphin release, reducing stress and promoting happiness, while also alleviating symptoms of anxiety and depression over time.
- Burns Calories by creating a calorie deficit through sustained moderate-intensity activity, supporting fat loss and weight management for the average person.
High Intensity Interval Training – 1 Zone 5 HIIT Session Per Week
Performing one Zone 5 High Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) session per week, involving short bursts of maximum effort (e.g., sprinting or cycling) followed by rest periods, significantly enhances your cardiovascular fitness, endurance, and metabolic health.
Gradually increasing the number of intervals and the length of maximum effort bursts over time ensures continued improvements.
- Improves Cardiovascular Health by enhancing heart efficiency, improving arterial function, and lowering blood pressure, reducing the risk of heart disease and stroke.
- Increases Fitness & Endurance by pushing your aerobic and anaerobic capacity, allowing you to sustain high-intensity activities longer and recover faster.
- Enhances Lung Health by improving oxygen utilization and increasing lung capacity through intense bursts, supporting better breathing during exertion.
- Boosts Mood by triggering a significant endorphin release during high-intensity efforts, reducing stress and enhancing happiness while combating anxiety.
- Increases VO2 Max by challenging your cardiovascular system at near-maximal effort, improving your body’s ability to use oxygen during exercise.
- Enhances Metabolic Health by improving insulin sensitivity and elevating your metabolic rate post-exercise, aiding fat loss and blood sugar regulation.
Rest Days – Why They Are Important
Rest days are a critical component of any fitness routine, allowing your body to recover and adapt to the physical demands of exercise. Without adequate rest, continuous training can lead to overtraining, increasing the risk of injury, fatigue, and burnout, which can hinder long-term progress and negatively impact overall wellbeing. For the average person, incorporating at least one to two rest days per week, or engaging in light active recovery like walking, ensures sustainable fitness gains and supports both physical and mental health.
- Reduces Injury Risk by allowing muscles and joints to recover, preventing overuse injuries from repetitive strain.
- Enhances Muscle Recovery by promoting repair of muscle fibers damaged during exercise, leading to stronger muscles over time.
- Improves Performance by restoring energy levels and reducing fatigue, allowing you to train harder in subsequent sessions.
Example of an Ideal Weekly Training Schedule
The image depicted below outlines an example of a what an ideal weekly training schedule may look like for the average person.
Most people should be aiming for around 2.5hrs of Zone 2 cardio, 2-3hrs of weight lifting and 15-30mins of High Intensity Interval Training every week. Depending on your health & fitness goals and available free time, you may need to increase or decrease training times accordingly.
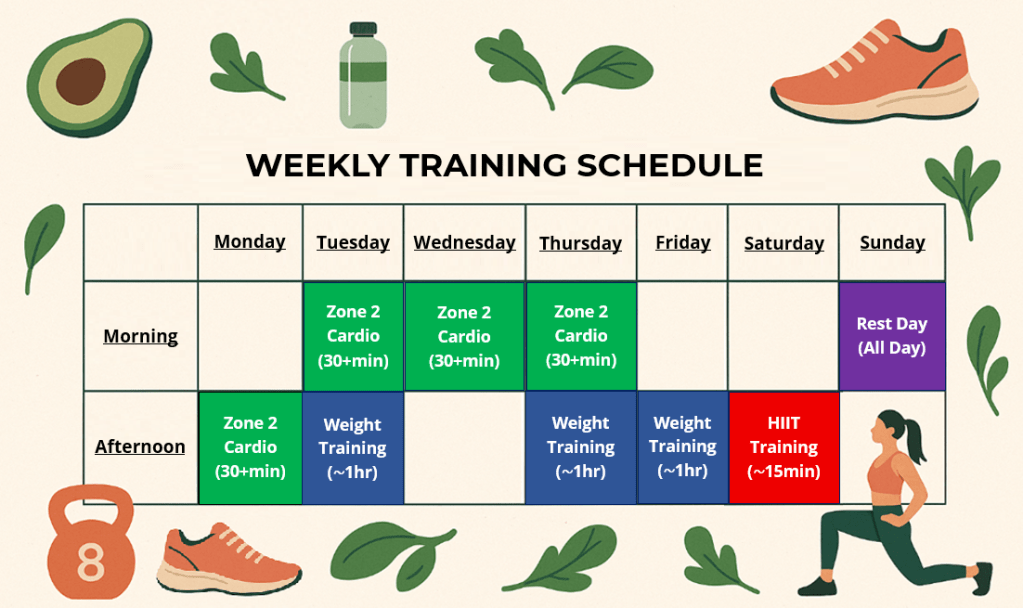
Note: There are 105 waking hours in a week if you consider 9hrs per night for sleep. This training schedule incorporates 6hrs of training total per week. That makes up a total of approximately 6% of your waking hours in a week. Most people should be able to dedicate this amount of time to exercise, keeping in mind that by doing so you will have more energy to do everything else in your life throughout the remainder of your week!
In Summary
A balanced fitness routine with strength training, cardio, HIIT, and rest days optimizes your health and performance. Strength training builds muscle and strength, cardio and HIIT boost endurance and heart health, while rest days ensure recovery and sustainability.
Incorporate three weekly strength sessions, four Zone 2 cardio sessions, one Zone 5 HIIT session, and at least one to two rest days. This approach enhances physical and mental wellbeing, supports fat loss, and promotes long-term fitness success.
FAQ
Can I skip HIIT if I’m short on time?
Yes. Focus on strength and Zone 2 cardio, but HIIT boosts fitness efficiently.
How do I adjust this for weight loss?
Increase Zone 2 cardio to 5 sessions weekly while maintaining strength training to preserve muscle.
Is this suitable for beginners?
Yes. Start with lighter weights and shorter cardio sessions, gradually increasing intensity.
