What is Protein Efficiency? | How Protein Quality is Measured | Animal vs Plant Protein Efficiency | Protein Scores for Common Foods | FAQ |
Quick Answer
Protein efficiency describes how well a protein source supports growth, repair, and health. Animal proteins are generally more efficient than plant proteins because they contain all essential amino acids and are more easily digested and absorbed.
Introduction
Not all proteins are equal when it comes to supporting your body’s needs. Protein efficiency measures how well a protein source is used by the body for growth and repair. This depends on its amino acid profile and how easily it is digested and absorbed. Understanding protein efficiency helps you choose the best foods for muscle building, recovery, and overall health.
Understanding Protein Efficiency and Quality
What is Protein Efficiency?
Protein efficiency refers to how effectively a protein source can be used by the body for growth, repair, and maintaining health. It is influenced by both the amino acid content and how well the protein is digested and absorbed. Higher efficiency means more of the protein you eat is turned into useful building blocks for your body.
- Protein efficiency can be measured based on amino acid composition and digestibility.
- High protein efficiency is important for muscle growth, recovery, and overall health.
How Protein Quality is Measured
Protein quality is now most commonly measured by two methods: PDCAAS (Protein Digestibility-Corrected Amino Acid Score) and DIAAS (Digestible Indispensable Amino Acid Score). These scores reflect both the amino acid content and how much of each amino acid is actually absorbed by the body.
- PDCAAS scores are based on amino acid content and overall digestibility, with a maximum score of 1.00.
- DIAAS is a newer method that measures digestibility at the end of the small intestine, giving a more accurate picture of how much protein is truly absorbed.
- Foods with higher scores are considered higher quality protein sources.
Animal vs Plant Protein Efficiency
Animal proteins are usually more efficient because they contain all essential amino acids and are highly digestible. Most plant proteins lack one or more essential amino acids and are less digestible due to anti-nutritional factors, though combining different plant sources can improve overall protein quality.
- Animal proteins like milk, eggs, and meat have higher efficiency and biological value.
- Plant proteins often have lower scores due to incomplete amino acid profiles and lower digestibility.
- Cooking and fermentation can improve the digestibility and efficiency of plant proteins.
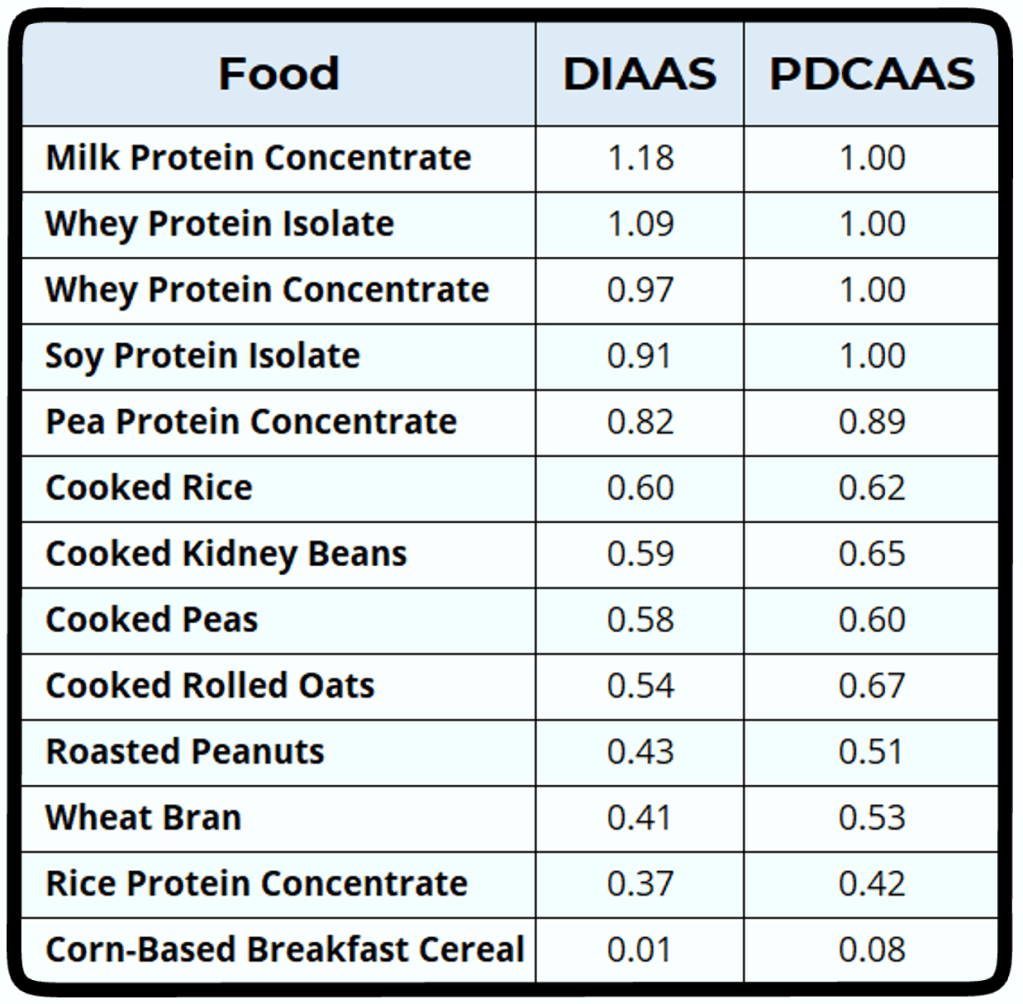
Protein Scores for Common Foods
The table below shows the Protein Digestibility-Corrected Amino Acid Score (PDCAAS) and Digestible Indispensable Amino Acid Score (DIAAS) scores for a range of protein sources. Higher scores mean more efficient protein for your body’s needs.
In Summary
Protein efficiency is about how well your body uses the protein you eat. Animal proteins are generally more efficient, but some plant proteins can be effective if they are combined and prepared well. Choosing high-quality protein sources supports muscle growth, recovery, and overall health.
FAQ
What makes a protein source efficient?
A protein is efficient if it contains all essential amino acids in the right amounts and is easily digested and absorbed by the body.
Why are animal proteins usually more efficient than plant proteins?
Animal proteins have complete amino acid profiles and are more digestible, while plant proteins often lack some essential amino acids and can be harder to digest.
Can plant proteins be as efficient as animal proteins?
Combining different plant proteins (like beans and rice) and using cooking or fermentation can improve their efficiency and nutritional value.
Do I need to worry about protein efficiency if I eat a varied diet?
If you eat a wide variety of protein sources, you are likely meeting your needs for essential amino acids and overall protein quality.
